In this blog post we set out to explain how high you can build your garden room under permitted development rules.
At Hawksbeck, we build most of our garden rooms under permitted development rules, but we still recommend that all our clients apply for a lawful development certificate on their proposed garden room. Our architects draw up plans and submit applications regularly for our clients. The certificate is issued by the council and is confirmation that your garden room has legal status. The certificate also confirms that your proposed garden room is built to the correct height. Should you wish to sell your house, solicitors representing purchasers will require documentary evidence that your garden room is lawful. It also provides necessary evidence that any works being undertaken are lawful if, for example, a neighbour were to make a complaint about the work.
The height restrictions under permitted development allow you to build;
- Garden Rooms, outbuildings and garages to be single storey with maximum eaves height of 2.5 metres and maximum overall height of four metres with a dual pitched roof or three metres for any other roof.
- Maximum height of 2.5 metres in the case of a building, enclosure or container within two metres of a boundary of the curtilage of the dwelling house.
What is the definition of height?
It’s important to understand what the Ministry of Housing Communities and Local Government defines as “Height” for Permitted development rights for householders. They define “Height” as:
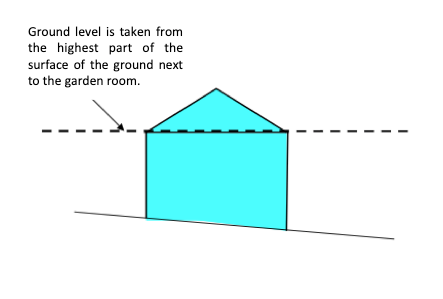
“References to height (for example, the heights of the eaves on a garden room) is the height measured from ground level. (Note, ground level is the surface of the ground immediately adjacent to the garden room in question, and would not include any addition laid on top of the ground such as decking. Where ground level is not uniform (for example if the ground is sloping), then the ground level is the highest part of the surface of the ground next to the building.)”
What can the maximum height of the eaves be in a garden room?
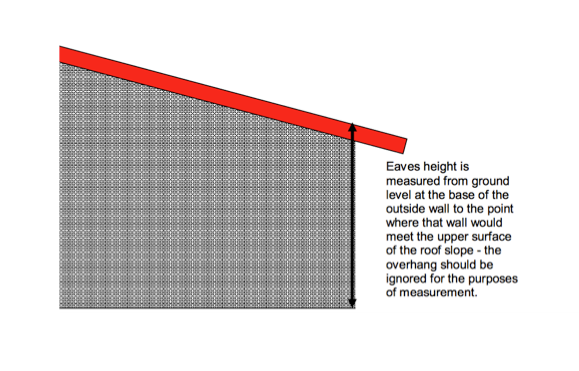
The eaves of a garden room will be the point where the lowest point of a roof slope, or a flat roof, meets the outside wall of the garden room. The maximum height of the eaves on any part of a garden room built under permitted development (irrespective of total height) is 2.5 metres. For example, on a garden room with a single-pitched roof, the 2.5 metres eaves limit and 3 metres maximum height limit would be as shown below.
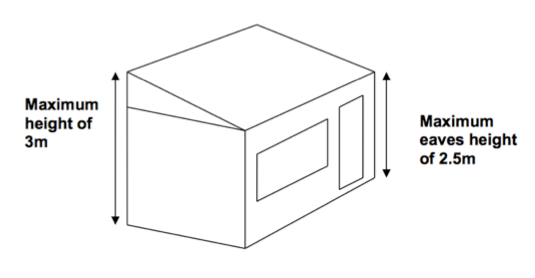
The following example shows the side view of a garden room with a pitched roof:
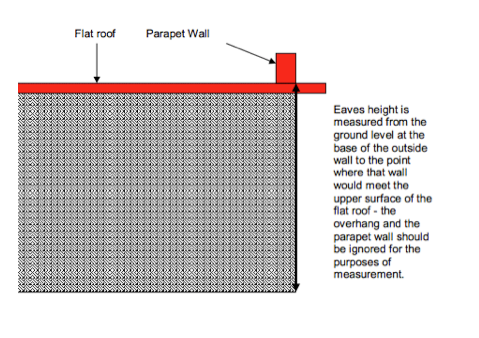
 Where there is a flat roof, a similar approach should be taken for measuring eaves:
Where there is a flat roof, a similar approach should be taken for measuring eaves:
Where a garden room is built on sloping ground, then the ground level is the highest part of the surface of the ground next to the building.
At Hawksbeck we are experts at navigating the permitted development rules. Our architects draw up plans and submit applications regularly for our clients. We believe it is vital to apply for a lawful development certificate as Permitted Development laws can change. So, what was legal and considered permitted development at the time of constructing your garden room, might not be years later when you come to sell your house. We think for the cost of £103 for lawful development application it is money well spent. Especially as we take all the hassle out of applying for a certificate as our architects are experts at drawing up plans and submitting applications on your behalf.
Have a question? Call our team today for further information on our garden rooms or for a free site survey.









